
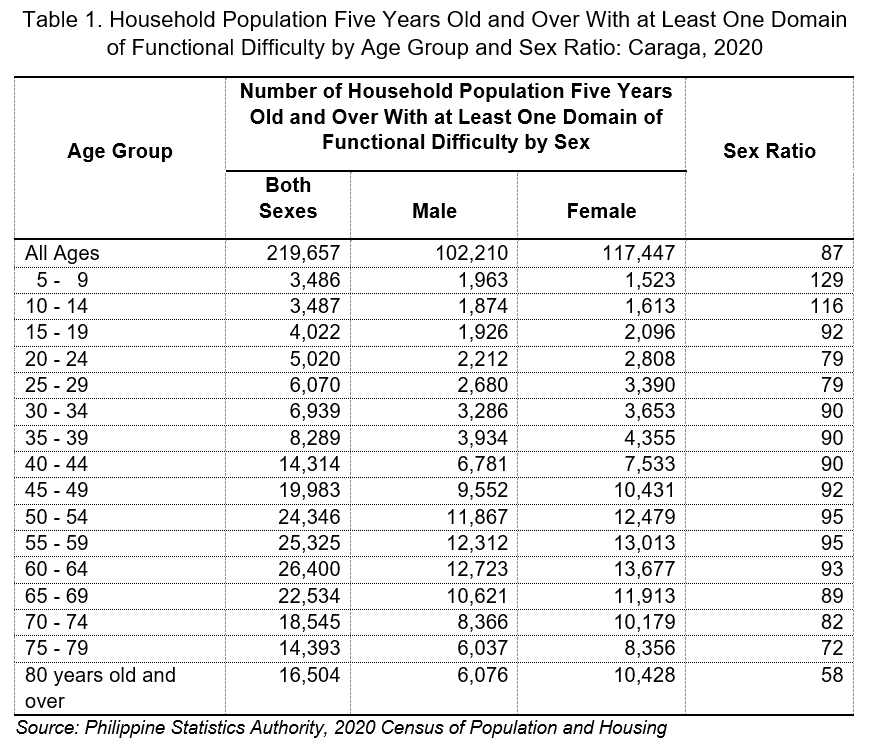
Based on the 2020 Census of Population and Housing (2020 CPH), of the 2.51 million household population five (5) years old and over, 219, 657 persons had at least one domain of functional difficulty, that is, any of the six (6) functional domains of seeing, hearing, walking or climbing steps, remembering or concentrating, self-caring (washing all over or dressing) or communicating. This is nearly nine (9) in every 100 persons (8.7%).
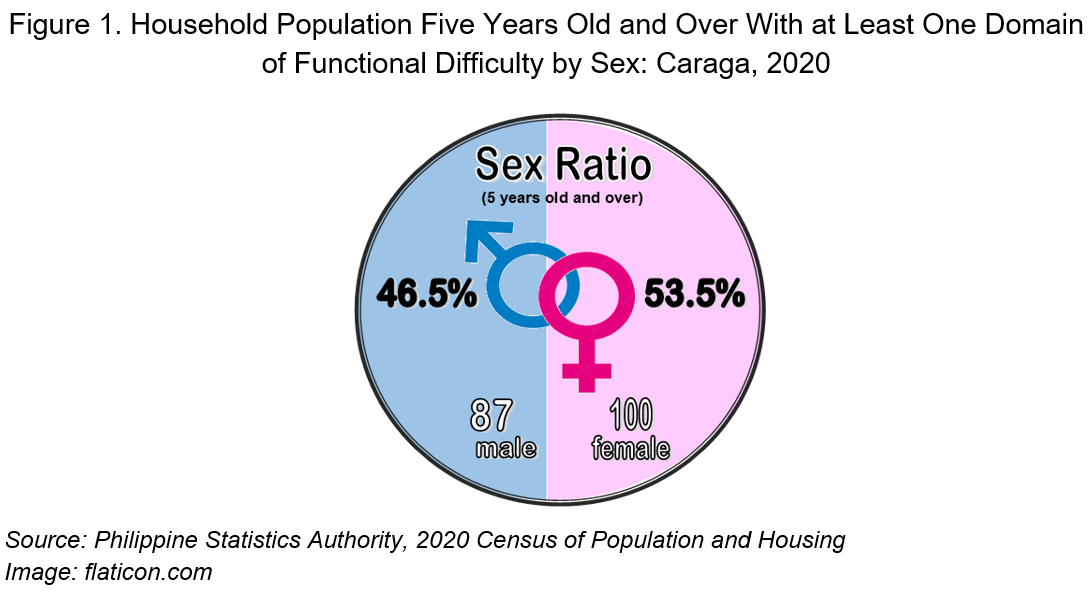
More females than males have at least one domain of functional difficulty
Of the 219,657 household population aged five (5) years old and over with at least one domain of functional difficulty, females accounted for 53.5 percent, while males comprised the remaining 46.5 percent. These figures resulted in a sex ratio of 87 males for every 100 females with at least one domain of functional difficulty. (Table 1)
Difficulty in seeing, even when wearing glasses, is the most common domain of functional difficulty
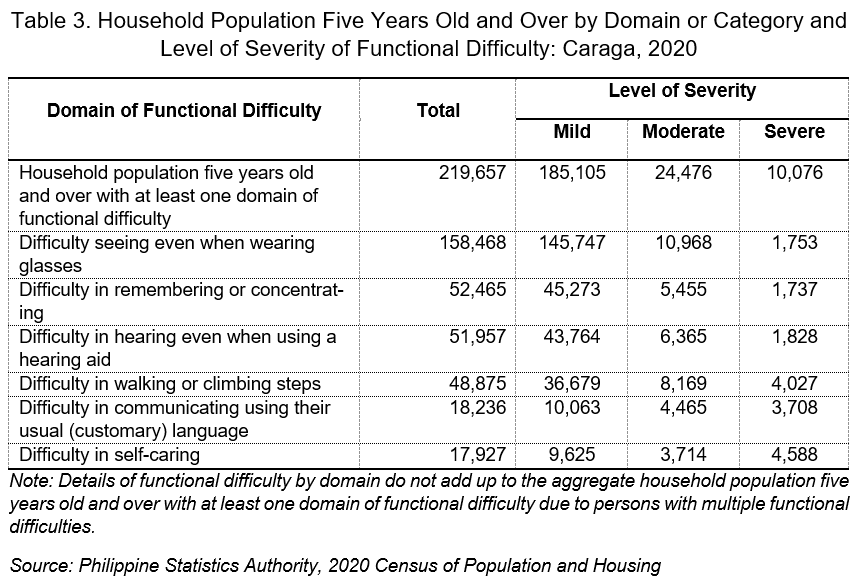
Of the 219,657 household population aged five (5) years old and over with at least one domain of functional difficulty, 72.1 percent reported having difficulty seeing even when wearing glasses. Further, those with difficulty in remembering or concentrating recorded 23.9 percent. This was followed by with difficulty in hearing even when using a hearing aid (23.7 percent), with difficulty in walking or climbing steps (22.3 percent), with difficulty in communicating using their usual (customary) language (8.3 percent), and with difficulty in self-caring (8.2 percent). (Table 2)


Of the 219,657 household population aged five (5) years old and over with at least one domain of functional difficulty, 84.3 percent were reported to have mild cases; 11.1 percent had moderate cases, and 4.6 percent had severe cases.
Mild case was highest among those with functional difficulty in seeing (145,747 cases). This was followed by those with difficulty in remembering or concentrating (45,273 cases), difficulty in hearing (43,764 cases), difficulty in walking or climbing steps (36,679 cases), difficulty in communicating (10,063 cases), and difficulty in self-caring (9,625 cases). (Table 3)
Among moderate cases, those with functional difficulty in in seeing were also the highest (10,968 cases), followed by those with difficulty in walking or climbing steps (8,169 cases), and those with difficulty in hearing (6,365 cases). (Table 3)
On the other hand, severe case of functional difficulty was highest among those with difficulty in self-caring (4,588 cases), followed by those with difficulty in walking or climbing steps (4,027 cases), and difficulty in communicating (3,708 cases).
TECHNICAL NOTES
The Philippine Statistics Authority conducted the 2020 Census of Population and Housing (2020 CPH) in September 2020, with 01 May 2020 as reference date.
The 2020 CPH was the 15th census of population and 7th census of housing that was undertaken in the Philippines since the first census in 1903. It was designed to take inventory of the total population and housing units in the country and collect information about their characteristics.
The Philippine Standard Geographic Codes as of April 2022 was used for the disaggregation of geographic levels of the 2020 CPH.
Data Limitation:
The statistics presented in this report were based on the information provided by the respondent or any responsible household member who may provide accurate answers to the questions and give correct information about all the household members; hence, it should be used with caution.
Methodology:
The population and housing censuses in the Philippines are conducted on a “de jure” basis, wherein a person is counted in the usual place of residence or the place where the person usually resides. The enumeration of the population and collection of pertinent data in the 2020 CPH referred to all living persons as of 01 May 2020.
Functional Difficulty were asked for household members five years and over. To identify household members who have functional difficulty, the respondents were asked, “Does have difficulty…?”. It is instructed to read out each kind of functional difficulty one by one.
a. seeing, even if wearing eyeglasses?
b. hearing, even if using a hearing aid?
c. walking or climbing steps?
d. remembering or concentrating?
e. self-caring (such as washing all over or dressing)?
f. communicating using his/her usual (customary) language?
Concept and Definition of Terms:
The Washington Group Short Set on Functioning (WG-SS)
The 2020 CPH adheres to the Washington Group Short Set on Functioning (WG-SS), which recommended the adoption of the concept of functional difficulty and developed questions that would address the issue of whether or not a person with a disability participates to the same extent as a person without a disability.
As an extended measure, an additional question recommended by the WG-SS was likewise adopted in the 2020 CPH to uncover a more detailed description of a person’s level of functioning. Thus, an answer scale of functional difficulty – “No difficulty”, “Some difficulty”, “A lot of difficulty”, and “Cannot do it at all” was included in the 2020 CPH to determine the severity of functional difficulty.
The Short Set on Functioning
The short set of functioning is comprised of questions on six core functional domains or categories: seeing, hearing, walking, cognition, self- care, and communication.
It is intended to focus the respondent on difficulties he or she may have that are the results of physical or mental health problem/s. Included are difficulties that occur within a health context rather than those caused by a lack of resources
Health refers to the general condition of the body or mind with reference to soundness, vitality, and freedom from disease.
Problem refers to the respondent’s perception of a departure from physical, mental or emotional well-being. This includes specific health problems such as a disease or chronic condition, a missing limb or organ or any type of impairment or physical or psychological symptoms. It also includes more vague disorders not always thought of as health-related such as senility, depression, developmental delay or intellectual impairment, drug dependency, accidental injuries, and others.
For the purpose of the 2020 CPH, functional difficulty is classified into six core domains or categories, namely:
a. Difficulty in seeing, even when wearing glasses
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have vision difficulties or problems seeing, even when wearing glasses (if they wear glasses).
Seeing refers to an individual using his/her eyes and visual capacity in order to perceive or observe what is happening around him/her.
Even when wearing glasses refers to difficulty seeing with glasses if the person has, and uses, them – NOT how vision would be if glasses, or better glasses, were provided or available to the one who needed them.
Included are problems in:
1. seeing things close up or far away; and
2. seeing out of one eye or only seeing directly in front but not to the sides.
Any problem with vision that the person considers a problem is captured.
b. Difficulty in hearing, even when using a hearing aid
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have some hearing limitations or problems of any kind with their hearing, even when using a hearing aid (if they wear a hearing aid).
Hearing refers to an individual using his/her ears and auditory (or hearing) capacity in order to know what is being said to him/her or the sounds of activity, including the danger that is happening around him/her.
Even when using a hearing aid refers to difficulty hearing with a hearing aid if the respondent has, and uses, that device – NOT how hearing would be if hearing aids, or better hearing aids were provided or available to the one who needed them.
Included are problems in:
1. hearing in a noisy or a quiet environment;
2. distinguishing sounds from different sources; and
3. hearing in one ear or both ears.
Any difficulty with hearing that is considered a problem is captured.
c. Difficulty in walking or climbing steps
The purpose of this question is to identify persons who have some limitations or problems of any kind getting around on foot.
Walking refers to the use of lower limbs (legs) in such a way as to propel oneself over the ground to get from point A to point B. The capacity to walk should be without assistance of any device (wheelchair, crutches, walker, and others) or human. If such assistance is needed, the person has difficulty walking.
Difficulty in walking includes those resulting from impairments in balance, endurance or other non-musculoskeletal systems, for example, blind people having difficulty walking in an unfamiliar place or deaf people climbing stairs when there is no lighting.
Included are problems in:
1. walking short (about 100 yards/meters) or long distances (about 500 yards/meters);
2. walking any distance without stopping to rest; and
3. walking up or down steps.
Any difficulty with walking (whether it is on flat land or up or down steps) that is considered a problem is captured.
d. Difficulty in remembering or concentrating (cognitive)
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have some problems with remembering or focusing attention that contribute to difficulty in doing their daily activities.
Remembering refers to the use of memory to recall incidents or events. It means the individual can bring to mind or think again about something that has taken place in the past (either the recent past or further back). With younger people, remembering is often associated with storing facts learned in school and being able to retrieve them when needed.
Remembering should NOT be equated with memorizing or with good or bad memories.
Concentrating refers to the use of mental ability to accomplish some tasks, such as reading, calculating numbers or learning something. It is associated with focusing on the task at hand in order to complete the task.
Included are problems in:
1. finding one’s way around, being unable to concentrate on an activity or forgetting one’s whereabouts or the date; and
2. problems remembering what someone just said or becoming confused or frightened about most things.
Any difficulty with remembering, concentrating or understanding what is going on around them that they or family members (if the family member is the respondent) consider a problem is captured.
Note: Difficulties remembering or concentrating because of common everyday situations such as high workload or stress, or as a result of substance abuse are excluded.
e. Difficulty with self-care such as washing all over or dressing
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have some problems with taking care of themselves independently.
Washing all over refers to the process of cleaning one’s entire body (usually with soap and water) in the usual manner for the culture.
The washing activity includes cleaning hair and feet, as well as gathering any necessary items for bathing such as soap or shampoo, a wash cloth or water.
Dressing refers to all aspects of putting clothing or garments on the upper and lower body, including the feet if culturally appropriate.
Included are the acts of gathering clothing from storage areas such as closet, dressers, securing buttons, tying knots, zipping, and others.
Washing and dressing represent tasks that occur on a daily basis and are considered basic, universal activities.
f. Difficulty in communicating using usual (customary) language
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have some problems with talking, listening, or understanding speech such that it contributes to difficulty in making themselves understood to others or understanding others.
Communicating refers to a person exchanging information or ideas with other people through the use of language.
Communication difficulties can originate in numerous places in the exchange process. It may involve mechanical problems such as hearing impairment or speech impairment, or it may be related to the ability of the mind to interpret the sounds that the auditory system is gathering and to recognize the words that are being used or an inability of the mind to compose a sentence or say a word even when the person knows the word and sentence. Included is the use of the voice for the exchange or using signs (including sign language) or writing the information to be conveyed. Included are problems making oneself understood, or problems understanding other people when they speak or try to communicate in other ways.
Note: Difficulty in understanding or being understood due to non-native or unfamiliar language is not included.
Note that the inclusion of assistive devices in the aforementioned domains was considered only in two domains – seeing and hearing, as limitations in these domains can often be easily overcome with the use of glasses or hearing aids, the use of which is common in most countries.
Functional Difficulty Status Indicators
Each question has four response categories, as follows:

The response categories capture the full spectrum of functioning from mild to severe. Using the WG-SS to define the category, with at least one functional difficulty includes those who responded with either “some difficulty”, “a lot of difficulty” or “cannot do it at all” to at least one of the six WG-SS questions.
On the other hand, without functional difficulty includes all those who responded only “no difficulty” to all six of the WG-SS questions.
Functional Difficulty Severity Indicators Based on the Level (Severity) of Difficulty
Severity labels are assigned based on the degree of difficulty indicated in the response option selected.
1. those who responded “cannot do it at all” to any functioning domain are labeled severe;
2. those who responded with “a lot of difficulty” are labeled moderate; and
3. those who responded with “some difficulty” are labeled mild.
Definition of Terms:
Household is a social unit consisting of a person or a group of persons who sleep in the same housing unit and have a common arrangement in the preparation and consumption of food.
Household population refers to all persons who are members of the household.
Sex is the biological and physiological reality of being a male or female.
Age refers to interval of time between the person’s date of birth and his/her last birthday prior to the census reference date. It is expressed in completed years or whole number.
Approved by:
(Sgd.)ROSALINDA C. APURA, D.M.
Regional Director, PSA-RSSO XIII
Telephone number: (085) 225-5219 / Telefax No. : (085) 815 – 4935
Email address: psacaraga_rsso13@yahoo.com.ph

